What Is BUG Rating in Outdoor Lighting? Backlight, Uplight, and Glare Explained
BUG rating is a key metric used in outdoor lighting design to control light pollution, glare, and unwanted spill. It helps designers, engineers, and inspectors understand how a fixture distributes light beyond the target area.
If you work with photometric plans, site lighting, or exterior fixtures, understanding BUG ratings is essential for code compliance and visual comfort.
What Does BUG Rating Mean?
BUG is an acronym that describes three types of unwanted light output from outdoor fixtures. Each component is measured separately to give a clear picture of fixture performance.

The Three BUG Components
Each BUG rating is expressed as three numbers, such as B2 / U1 / G3. Lower values mean better control of light.
- Backlight (B): Light emitted behind the fixture.
- Uplight (U): Light emitted above the horizontal plane.
- Glare (G): High-angle brightness that causes visual discomfort.
BUG ratings are defined by the IES (Illuminating Engineering Society) and are commonly used in zoning ordinances and outdoor lighting standards.
How BUG Ratings Affect Outdoor Lighting Design
BUG ratings help ensure outdoor lighting provides visibility and safety without creating excessive glare or light trespass onto neighboring properties.
- Limits light pollution and sky glow
- Improves visual comfort for pedestrians and drivers
- Supports compliance with local lighting codes
Lighting Zones and BUG Limits
Outdoor sites are classified into Lighting Zones (LZ0–LZ4). Each zone sets maximum allowed BUG values based on environmental sensitivity.
- LZ0–LZ1: Very low BUG values required
- LZ2: Typical residential environments
- LZ3–LZ4: Commercial and urban areas
The following tables display the thresholds for each subzone.
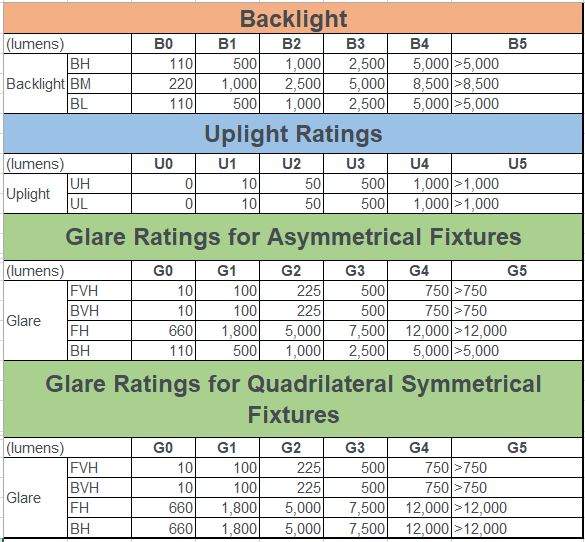
BUG ratings are always evaluated using a fixture’s IES file and verified during photometric calculations.
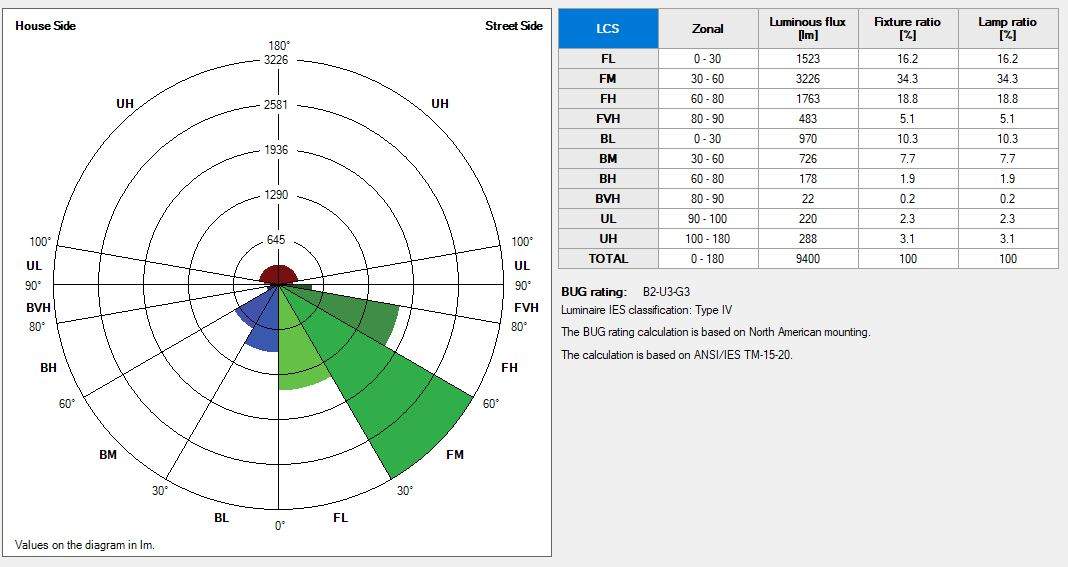
Example: BUG Rating in a Real Project
In this residential exterior example, three wall-mounted fixtures were analyzed using photometric software and the manufacturer’s IES data.
- Location: Residential facade
- Lighting Zone: LZ2
- Measured BUG Rating: B2 / U3 / G3
This rating shows moderate uplight and glare, which may be acceptable in residential zones but would likely require adjustment in more sensitive environments.

Get a Professional Photometric Plan
We create accurate photometric plans that verify BUG ratings, lighting levels, and code compliance.
Final Takeaways
BUG ratings are a critical part of modern outdoor lighting design. They help control glare, limit light pollution, and ensure fixtures perform as intended.
If you need help verifying BUG ratings or preparing a compliant photometric plan, Stetra Lighting can support your project from fixture selection to final approval.
